In their natural environment, wild game species have little need for supplementary feeding. This is because their free-ranging habits enable them to pursue more nutritious grazing and therefore satisfy their nutrient requirements. The advent of game farming, however, has resulted in wild animals being confined to camped-off areas. This, combined with the desire for more prolific breeding, has necessitated the use of supplementary feeding when nature cannot supply. In the case of boma-fed and stabled animals, their total feed requirements have to be met.
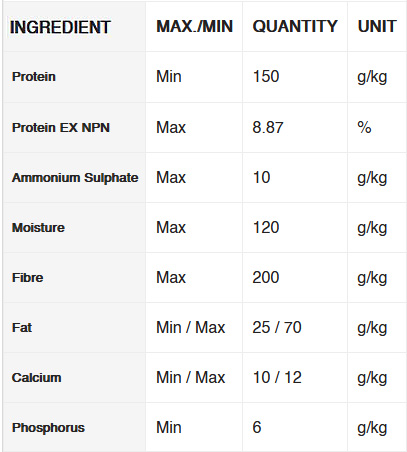
Epol game pellets are formulated to ensure the optimal amounts of digestible protein, amino acids, minerals, trace minerals and vitamins.
Reference used: National Research Council’s work on beef, dairy cows, horses, camelids, sheep, goats and cervids
Our Focus:
- Supplementation of nutritional deficiencies in natural pasture.
- Supplementation and/or feeding of game in captivity (bomas, auction camps, zoos).
- Attracting game to observation points, or out of specific habitat areas that require recuperation.
- The use of game animal feed supplements together with roughage when natural forage is in short supply.
Feeding Tips:
- Supply ample clean water in shallow troughs; game species are sensitive to any changes in water quality.
- Provide free access to high quality, palatable grass hay or lucerne or a combination of both, depending on the game species’ feeding habits
- Ensure a gradual introduction of Epol Game feeds or self-mix feeds over a 4- to 5-week period.
- Epol Game cubes/pellets should never be supplied ad lib. This will ensure that individual dominant or aggressive animals don’t over consume.
- Supplementation on natural pasture, or to attract game to observation points, should not exceed 0.8% of the body weight (animals heavier than 100 kg), which is approximately 30% of the animal’s dry matter intake. This will help to avoid substitution of the natural pasture by pellets/cubes.
- Mineral supplementation should occur throughout the year, in the form of palatable salt/mineral licks and suitable water additives.
- Game species that are under social, environmental or nutritional stress succumb to parasite infestation. Therefore, medication with anthelmintics should form part of the management strategy.